Hearing tests, also known as audiometric tests, are essential tools for assessing a person’s hearing capability. These evaluations help determine the range and nature of hearing loss and are critical in devising appropriate treatment strategies including, but not limited to, hearing aids, cochlear implants, and other supportive hearing devices. Below is a detailed exploration of the various types of hearing tests and their importance in diagnosing and managing hearing impairments.
Pure-Tone Testing
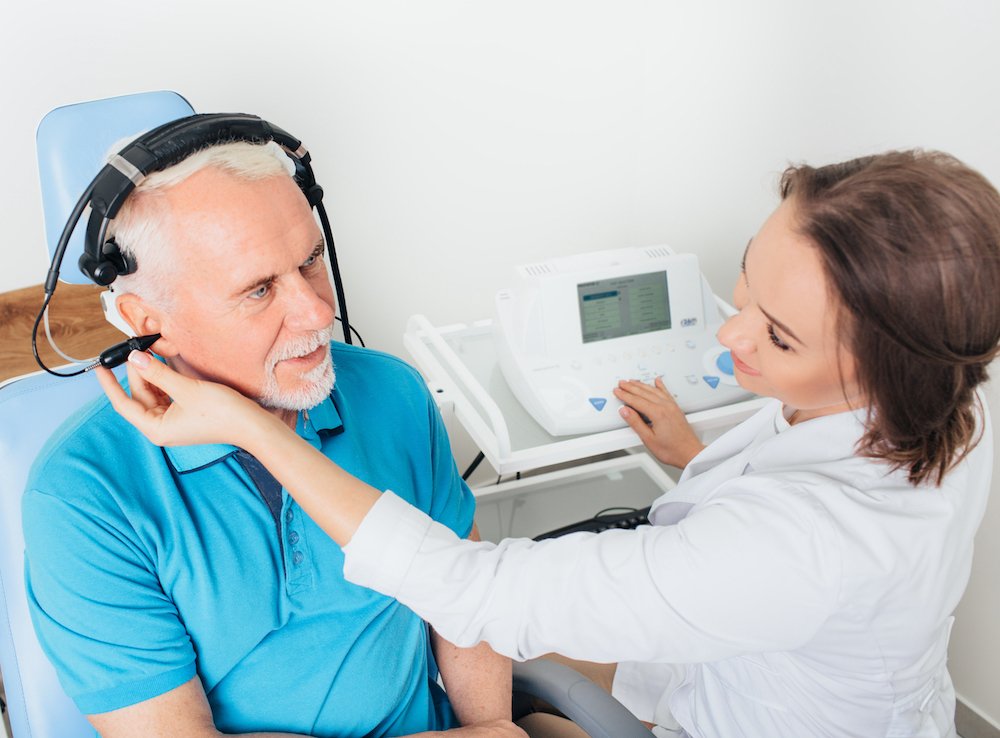
Pure-tone audiometry is the cornerstone of hearing tests. It involves the individual listening to specific tones at different pitches (frequencies) and volumes (decibels) through headphones. The test targets each ear individually, charting the quietest sound that can be heard at least 50% of the time. This method helps identify the quietest level of sound a person can detect at various frequencies and is pivotal in diagnosing the degree of hearing loss.
Speech Testing
Speech audiometry provides a more practical assessment of hearing loss by measuring the ability to hear and understand speech. This test is not only about detecting sounds but also about clarity of understanding. During the test, the individual is required to repeat words spoken at various volume levels and in different conditions, which may include a quiet or noisy background. The results help determine the softest level at which a person can understand speech and how background noise affects their speech understanding.
Middle Ear Tests
These tests assess the health and functionality of the middle ear. The most common middle ear test is tympanometry, which evaluates the eardrum and the conduction bones by creating variations in air pressure in the ear canal. This test helps detect problems like fluid in the middle ear, perforated eardrum, or ossicle bone issues, which can all contribute to hearing loss.
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) Testing
Otoacoustic emissions testing is an objective hearing test that may be administered within the first days of life as part of newborn hearing screenings. This test measures sound waves produced in the inner ear, known as otoacoustic emissions, which occur when the cochlea is healthy and functioning properly. The absence of these emissions can indicate blockage or damage to the inner ear, even if the outer and middle ears appear normal.
Importance of Hearing Tests
Hearing tests are vital not only for detecting hearing loss at an early stage but also for planning effective treatment and rehabilitation. For children, early diagnosis and intervention can significantly impact language development and academic achievement. In adults, timely management of hearing loss can improve quality of life and reduce risks associated with hearing impairments, such as social isolation and cognitive decline.
Conclusion
Hearing tests are a fundamental aspect of auditory health care, providing essential data that specialists use to tailor interventions effectively. Whether it’s identifying the type and extent of hearing loss or monitoring an ongoing condition, hearing tests offer invaluable insights into one’s auditory health status. Regular hearing evaluations are recommended for individuals who are exposed to prolonged loud noise, experience tinnitus, struggle with speech comprehension, or simply as part of routine health check-ups in older adults.
Understanding the full spectrum of hearing tests and their benefits can empower individuals to seek timely medical advice and enjoy the full range of sounds that life has to offer.
Leave a Reply